- ANU Library
- LibGuides
- new production templates
- Law
- The Australian Legal System
Australia is a parliamentary democracy. The Australian Constitution of 1901 established a federal system of government in Australia. Under this system, powers are distributed between a national government (the Commonwealth) and the six States. The Constitution defines the boundaries of law-making powers between the Commonwealth and the States/Territories.
As well as the six States (New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria and Western Australia) there are three self -governing territories - Australian Capital Territory, Northern Territory, and Norfolk Island.
The legal system, a common law system, was inherited from England at the time of colonisation. The two major sources of Australian law are:
Cases - the decisions made by judges in the courts; and
Legislation - the legal rules made by parliament and by those to whom parliament has delegated authority.
(from Parliament an Overview)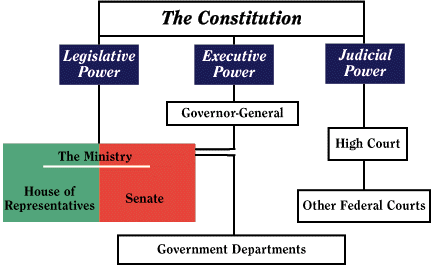
 Introducing the law, 7th ed by Heilbronn, Gary N et al
Introducing the law, 7th ed by Heilbronn, Gary N et al Law and justice in Australia : foundations of the legal system, 3rd ed by Prue Vines
Law and justice in Australia : foundations of the legal system, 3rd ed by Prue Vines Laying down the law, 10th ed
Laying down the law, 10th ed Understanding law: an introduction to Australia's legal system, 8th ed by Richard Chisholm and Garth Nettheim
Understanding law: an introduction to Australia's legal system, 8th ed by Richard Chisholm and Garth Nettheim Understanding the Australian legal system, 7th ed by John Carvan
Understanding the Australian legal system, 7th ed by John CarvanPage Contact: ANU Library Communication Team
+61 2 6125 5111
The Australian National University, Canberra
TEQSA Provider ID: PRV12002 (Australian University) |
CRICOS Provider Code: 00120C |
ABN: 52 234 063 906
Contact ANU |
Copyright |
Disclaimer |
Privacy |
Freedom of Information

